- Vroom Expectancy Model
- Criticism Of Vroom 27s Expectancy Theory Of Motivation Interviewing
- Criticisms Of The Expectancy Theory
- Criticism Of Vroom 27s Expectancy Theory Of Motivation Theory
The Expectancy Theory of Victor Vroom (1964) deals with motivation and management, and how managers may secure a motivated workforce. The essence of this theory is that actions and behaviors of individuals are taken based on an objective to maximize pleasure and minimize pain. According to which of the following theories of motivation is an individual's perceptions of inputs and outputs the primary determining factor as to whether inequity exists. A) Equality b) Expectacy c) Equity d) Equilibrium. Alderfer developed theory to address criticisms of , recognizing that individuals work to satisfy. Vroom’s expectancy theory differs from the content theories of Maslow (1943), Alderfer (1969), Herzberg (1959), and McClelland (1961). The fundamental difference is that Vroom’s expectancy theory does not provide specific propositions on what motivates an organisation’s members.
This theory is based on the premises that an employee will be motivated to put forth a higher level of effort when they know that it will yield high performance and will result in better rewards. In this theory, an individual selecting the behavior is based on the desirability of outcomes. This process involves mental processes regarding choice. This tells us the process of an individual undergoing to make choices. It was first proposed by Victor Vroom of the Yale School of Management. Victor H. Vroom (1964) defines motivation as a process governing choices among alternative forms of voluntary activities, a process controlled by the individual. Individual makes choices based on the expectations of the expected results of a given behavior.
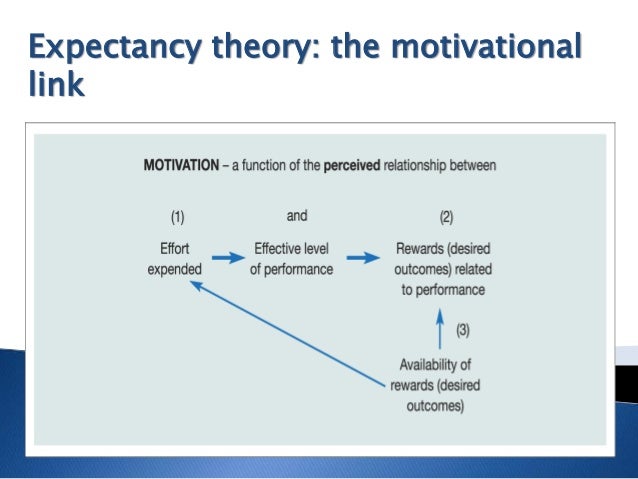
Key Elements of Vroom’s expectancy theory are:
1) Expectancy: efforts -> performance
It is the belief that the effort of an individual will help in achieving the desired performance.
a) Self Efficacy- It is the belief of an individual to perform a certain behavior. They will assess themselves and know whether they have the required skills or not.
b) Goal difficulty- When the goals of the organization are set too high or expectations of the performance, it will result in low expectancy. This occurs when an individual start thinking that the goal is not attainable.
c) Perceived Control- Individual must believe that they have some control over the outcome of a behavior. When they believe that it is out of the control then the motivation level is low.
2) Instrumentality: performance -> outcome
It believes that reward will be received when the performance expectation is achieved. Reward could be anything, increase in salary or promotion etc. Instrumentality is low when same reward is given for all performances. Another way of instrumental outcome work is commission. Commission is directly correlated with the outcome. More the outcome, more the commission.
Vroom Expectancy Model
3) Valence V(R)
Value an individual place on the expected outcome, which is based on their needs, goals or objectives. It is characterized by the extent to which a person values a given outcome. It is not an actual level of satisfaction rather an expected level of satisfaction of a particular outcome.
The valence refers to the value the individual personally places on the rewards. -1 →0→ +1
To attain the positive valence, person must prefer attaining the outcome to not attaining it.

Criticism of Vroom’s Expectancy theory
1) Edward Lawler claims that the simplicity of expectancy theory is deceptive because it assumes that if an employer makes a reward, employees will increase productivity to obtain the reward. However, this is only possible when if the employee thinks that it is beneficial to their immediate needs.
Criticism Of Vroom 27s Expectancy Theory Of Motivation Interviewing
2) If anyone is transferred to other places due to the promotion and if that place is far away from the resident place then the employee will not be motivated and the result will be other way round.
3) W.F. Maloney and J.M. McFillen found that expectancy theory could explain the motivation of those individuals who were employed by the construction industry. For instance, they used worker expectancy and worker instrumentality. Worker expectancy is when supervisors create an equal match between the worker and their job. Worker instrumentality is when an employee knows that any increase in their performance leads to achieving their goal.
Few important topics related Employee motivation

- Motivation Theories
- Methods of motivating employees
- The Needs Theory
- ERG Theory of Motivation
- Acquired Needs Theory
- The Equity theory of Motivation
- Vroom’s Expectancy Theory
- Thorndike's Reinforcement Theory
- Locke’s Goal Setting Theory
- Self Determination
- Cognitive Evaluation Theory
- Reward Systems & Employee Behavior
Victor Vroom propounded a process theory namely Expectancy theory to explain motivation. The central concept of the Vroom Expectancy theory of motivation is that individual is motivated and the strength of his action depends on close association between his preference to a specific outcome and the actual outcome. The theory established relationship between effort, performance and rewards. According to expectancy theory, motivation is the result of the sum of the products of valence, instrumentality and expectancy. It can be stated in the form of the following mathematical formula.
Motivation = Σ( Valence X Instrumentality X Expectancy)
Relationship between Effort, Performance and Rewards
- Effort-Performance Relationship: It is the probability perceived by the individual that exerting a given amount of effort leads to performance.
- Performance-Reward Relationship: This is the degree to which the individual believes that performing at a particular level will lead to the attainment of a desired outcome.
- Rewards-Personal Goals Relationship: It is the degree to which organisational rewards satisfy an individual’s personal goals or needs and the attractiveness of those potential rewards for the individuals
Vroom Expectancy Theory: Valence, Instrumentality and Expectancy
- Valence: Valence is the strength of an individual’s preference for a particular outcome. Every individual believes that his effort leads to certain definite outcome. This is expected utility or value. The greater the strength or the expectation of the outcome the greater would be the level of motivation. The valence can be positive or negative. It is positive when employee has a strong preference to reward. It will be zero if he is indifferent. Similarly, it will be negative if employee does not prefer to attain the outcome.
- Instrumentality: Instrumentality refers to the strength of the belief about the certainty of outcome. Thus, it is the expression of probability between performance and reward. This varies between ± 1. The performance reward relationship is positive, in case of positive instrumentality and vice versa.
- Expectancy: Expectancy is the belief that effort will lead to outcome and performance. Therefore, expectancy determines the strength of performance rather than the outcome. It is based on the self-efficacy. Employee with a high level of self-efficacy is more likely to believe that exerting effort will result in satisfactory performance. A high level of self-efficacy has high expectancy, while low level of self-efficacy has low expectancy. Persons suffering from low level of self-efficacy exhibit a phenomenon known as ‘imposter phenomenon’. This means that individuals are capable, as they appear to be. They are afraid of their inferiority, which may be revealed in public if they exert high effort. Imposters have low expectancy, as they believe that they lack the necessary competence. Expectancy is evaluated as a probability. It varies from 0 to 1. Zero is associated with complete uncertainty. As the performance is assured the expectancy rises and it will be high if the performance is certain. It is interesting to note that both internal and external environment influence expectancy.
Criticisms Of The Expectancy Theory
The Level of Motivation
Criticism Of Vroom 27s Expectancy Theory Of Motivation Theory
| Valence | Instrumentality | Expectancy | Motivation |
| High | High | High | Strong motivation |
| Low | High | High | Moderate motivation |
| High | Low | High | Strong avoidance |
| Low | Low | High | Moderate avoidance |
| High | High | Low | Moderate motivation |
| Low | High | Low | Weak avoidance |
| High | Low | Low | Moderate avoidance |
| Low | Low | Low | Strong avoidance |
We hope you liked this article. Here are few useful articles for you to read next:
Tags:victor vroom expectancy theory, vroom motivation theory, expectancy theory, victor vroom theory, expectancy theory of motivation, vroom expectancy motivation theory, expectations theory formula, vroom expectancy theory pdf